The Israel Defense Forces (IDF) has destroyed the ability of Lebanese Hezbollah to conduct ground attacks into Israel, according to unspecified senior IDF officers.[1] The IDF has conducted clearing operations targeting Hezbollah capabilities and infrastructure across southern Lebanon to this end since October 1. These clearing operations have involved destroying Hezbollah sites and seizing tens of thousands of weapons.[2] The IDF announced on November 10, for instance, that it destroyed a major underground complex near the Israel-Lebanon border that was meant to support Hezbollah incursions into northern Israel.[3] The IDF has especially focused on degrading the Hezbollah Radwan special operations forces during the clearing operations.[4] Eliminating the threat of ground attacks is critical to achieving the stated Israeli war aim of returning displaced civilians safely to their homes in northern Israel.
Several senior IDF officers calculate that displaced civilians can return even without a ceasefire agreement with Hezbollah.[5] The IDF officers told Israeli Army Radio that, without a ceasefire agreement, three Israeli divisions would deploy to the Israel-Lebanon border after concluding clearing operations in southern Lebanon.[6] These divisions would give the IDF the option to attack and disrupt any Hezbollah efforts to re-entrench in southern Lebanon.[7] This Israeli plan is similar to the US-drafted ceasefire proposal, which would permit the IDF to operate in southern Lebanon against any Hezbollah activity there.[8]
Hezbollah continues to threaten civilians in northern Israel with relatively long-range weapons, however. Unspecified senior IDF officers acknowledged this enduring threat in remarks to Israeli Army Radio.[9] The IDF officers said that, while Hezbollah can no longer conduct a ground attack in Israel, Israeli forces along the Israel-Lebanon border must be prepared to intercept Hezbollah fire into northern Israel.[10] Some of the anti-tank missiles that Hezbollah has, such as Kornet missiles, have ranges up to five kilometers.[11] Under CTP-ISW’s layer of current assessed Israeli advances, the IDF would need to clear areas of southern Lebanon that it has not yet cleared in order to push Hezbollah more than five kilometers from northern Israel.[12]
Longer-range Hezbollah munitions, such as drones, missiles, and rockets, similarly continue to threaten residents of northern Israel, even though Israeli operations have likely diminished Hezbollah stockpiles considerably. Hezbollah rocket attacks injured at least six Israeli civilians in northern Israel on November 10, for example.[13] IDF officers have estimated that Israeli air operations have degraded Hezbollah missile and rocket capabilities to the point that Hezbollah has to be ”economical” in its use of munitions. The IDF also recently estimated it has destroyed 70 percent of Hezbollah’s pre-October 7, 2023 drone stockpile.[14] Although Hezbollah has launched a daily average of 44 rockets into Israel in November 2024, the volume of rocket fire is short of pre-war estimates of Hezbollah’s capabilities, which had indicated that Hezbollah may launch up to 1,500 missiles and rockets daily in the event of war.[15]
Hezbollah appears to still be suffering from the internal disruption imposed by Israeli operations. The IDF has continued targeting tactical-level Hezbollah commanders in southern Lebanon, which CTP-ISW has assessed may be diminishing the combat effectiveness of some Hezbollah units.[16] Unspecified Arab and Israeli officials told the Wall Street Journal that Israel has killed several Hezbollah commanders before they were able to reach their field positions in southern Lebanon.[17] The replacements to these commanders are less familiar with southern Lebanon’s terrain and their units’ fighters, according to the officials.[18] This disruption has likely impeded Hezbollah’s ability to conduct effective and organized defenses against advancing Israeli forces. Israeli soldiers said that Hezbollah fighters are still offering resistance but are leaning into “guerilla tactics” by waiting inside homes and tunnels—rather than operating at a greater scale across large groups of fighters.[19]
The IDF has seized over 66,000 Hezbollah weapons, including almost 6,000 explosive devices and over 3,000 anti-tank guided missiles.[20] IDF officers and other personnel said that the equipment was all “relatively new” and included new night-vision goggles and medical kits.[21] CTP-ISW has previously assessed that the discovery of high-end weapons systems and equipment suggests that Hezbollah fighters fled their positions rather than seeking to delay Israeli forces in an organized fashion by slowly withdrawing.[22]
Israeli Army Radio reported on November 10 that Israeli Strategic Affairs Minister Ron Dermer had traveled to Russia in recent days to discuss a ceasefire agreement in Lebanon.[23] The visit reportedly occurred after the IDF strikes into Iran on October 25.[24] Israeli Army Radio reported that Russia is expected to play a crucial role in the implementation of a potential ceasefire agreement by preventing Hezbollah from rearming.[25] Israeli media reported that a Russian delegation previously visited Israel on October 24, according to a source in Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s office.[26] It is unclear why Russia would prevent Hezbollah from rearming given that Russian forces in Syria have enabled Hezbollah to arm up to this point by allowing Iranian material transfers through Syria to Lebanon.[27]
Key Takeaways:
Lebanon: The IDF has destroyed the ability of Lebanese Hezbollah to conduct ground attacks into northern Israel, according to senior IDF officers. Hezbollah continues to threaten civilians in northern Israel with relatively long-range weapons, however.
Lebanon: Lebanese Hezbollah appears to still be suffering from internal disruption imposed by Israeli operations. This disruption has likely impeded the ability of Hezbollah to conduct an effective and organized defense against IDF operations in southern Lebanon.
Lebanon: Russia is expected to contribute to the implementation of a possible ceasefire in Lebanon. It is unclear why Russia would do so given that it has enabled Hezbollah to arm itself by allowing Iranian material transfers through Syria to Lebanon.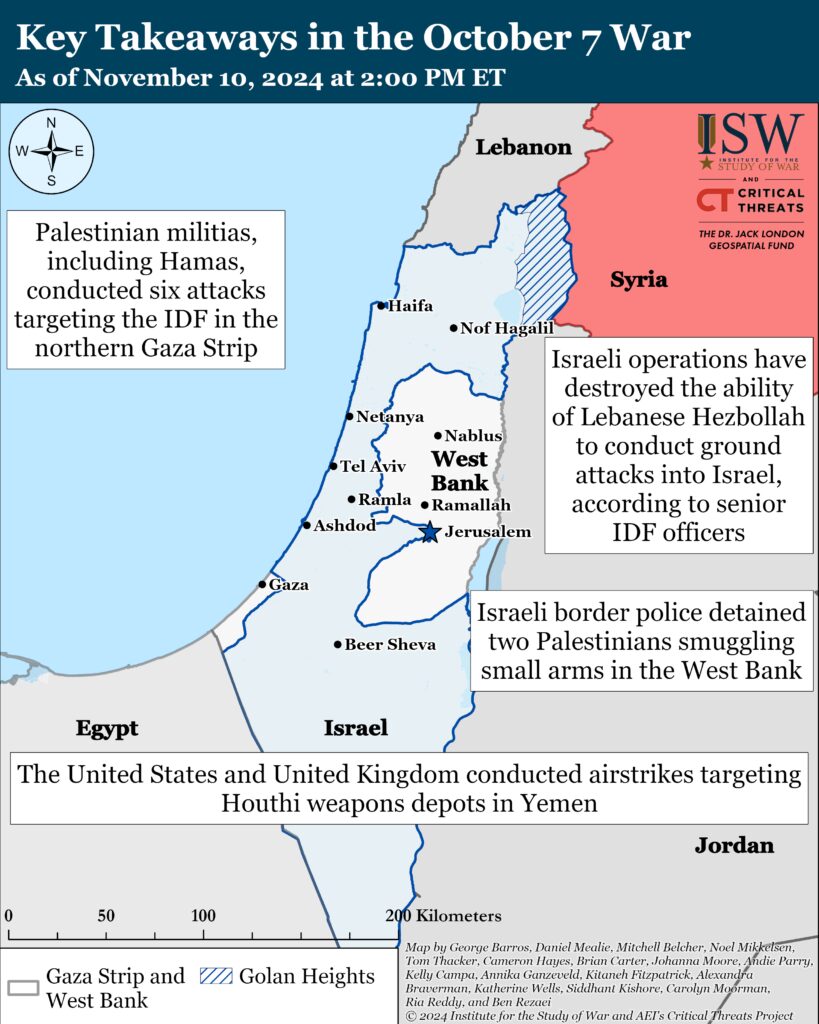
Gaza Strip:
Axis of Resistance objectives:
Erode the will of the Israeli political establishment and public to sustain clearing operations in the Gaza Strip
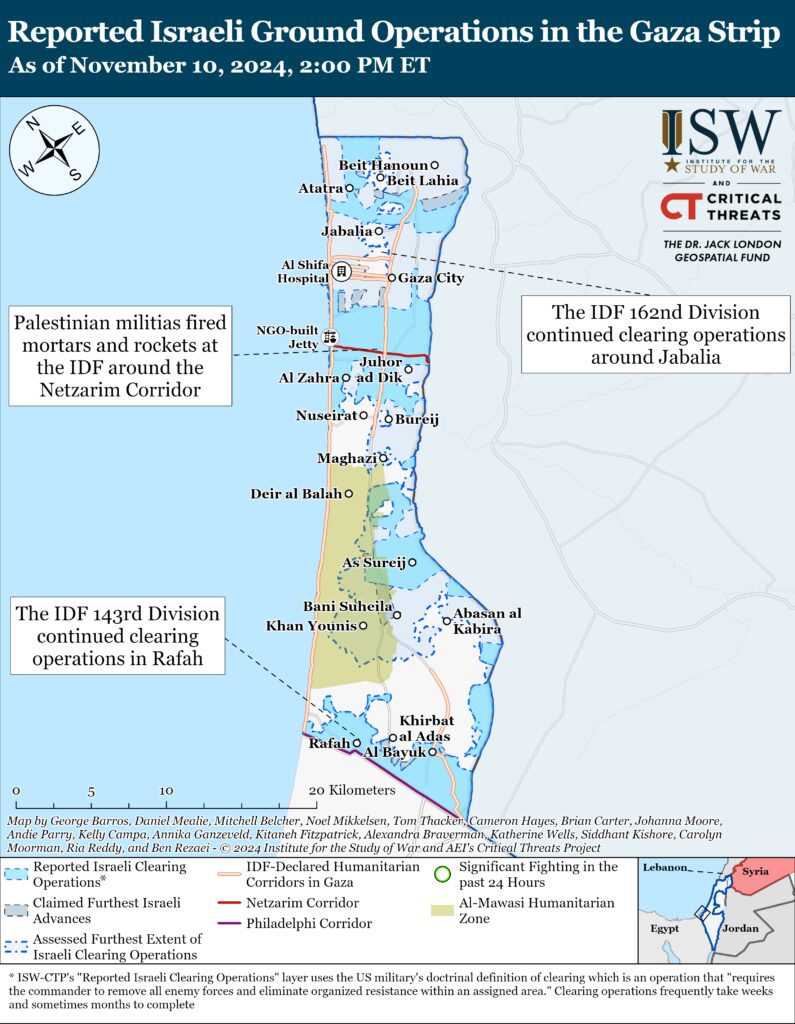
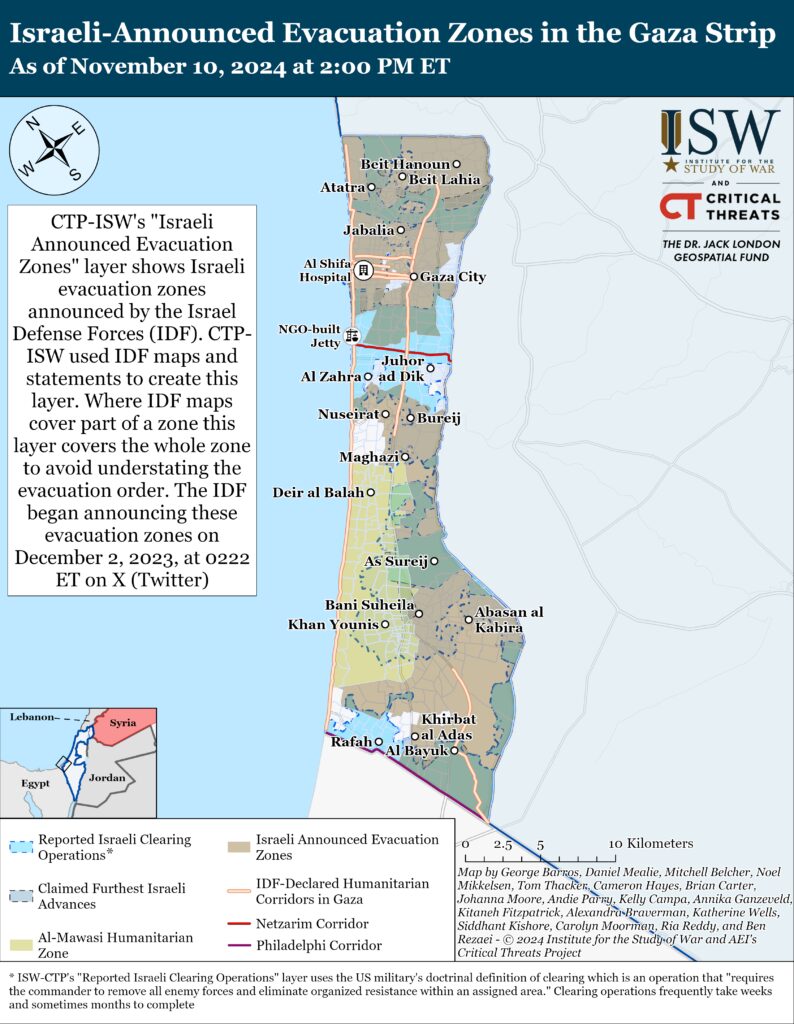
Reestablish Hamas as the governing authority in the Gaza StripThe IDF 162nd Division continued clearing operations around Beit Lahia and Jabalia in the northern Gaza Strip on November 10. The IDF killed dozens of militia fighters and destroyed militia infrastructure, including a weapons depot.[28] The IDF 900th Infantry Brigade (162nd Division) targeted Palestinian fighters in Beit Lahia in airstrikes and close-range combat.[29] The brigade specializes in operations in urban environments and is well-suited to destroy militia cells within Jabalia City and refugee camp.[30]
Palestinian militias, including Hamas, conducted at least six attacks targeting the IDF in Beit Lahia and Jabalia.[31] Hamas attacked 15 Israeli soldiers with rocket-propelled grenades and small arms in Beit Lahia.[32] A Palestinian journalist reported Israeli armor movement and artillery shelling in Beit Lahia and Jabalia.[33]
Several Palestinian militias fired mortars and rockets targeting the IDF around the Netzarim Corridor on November 10.[34]
The IDF 143rd Division continued clearing operations in Rafah on November 10.[35] The IDF 933rd Brigade (143rd Division) destroyed militia infrastructure, killed Palestinian fighters, and located weapons in Rafah.[36]
West Bank
Axis of Resistance objectives:
Establish the West Bank as a viable front against IsraelIsraeli forces engaged Palestinian fighters in Nablus, West Bank, on November 10. The al Aqsa Martyrs’ Brigades fired small arms and detonated improvised explosive devices targeting Israeli forces in several parts of Nablus.[37]
Israeli border police detained two Palestinians smuggling small arms near Jericho, West Bank. The border police seized 13 M16 rifles and other weapon parts.[38] This incident comes as the IDF is establishing a new division to counter threats, including arms smuggling, around the Israel-Jordan border.[39] Iran has increased its efforts to smuggle weapons and other materiel into the West Bank in recent years but has limited success.[40] Most engagements between Israeli forces and Palestinian militias in the West Bank use small arms and rudimentary improvised explosive devices.
Northern Israel and Lebanon
Lebanese Hezbollah objectives:
End Israeli operations in the Gaza Strip
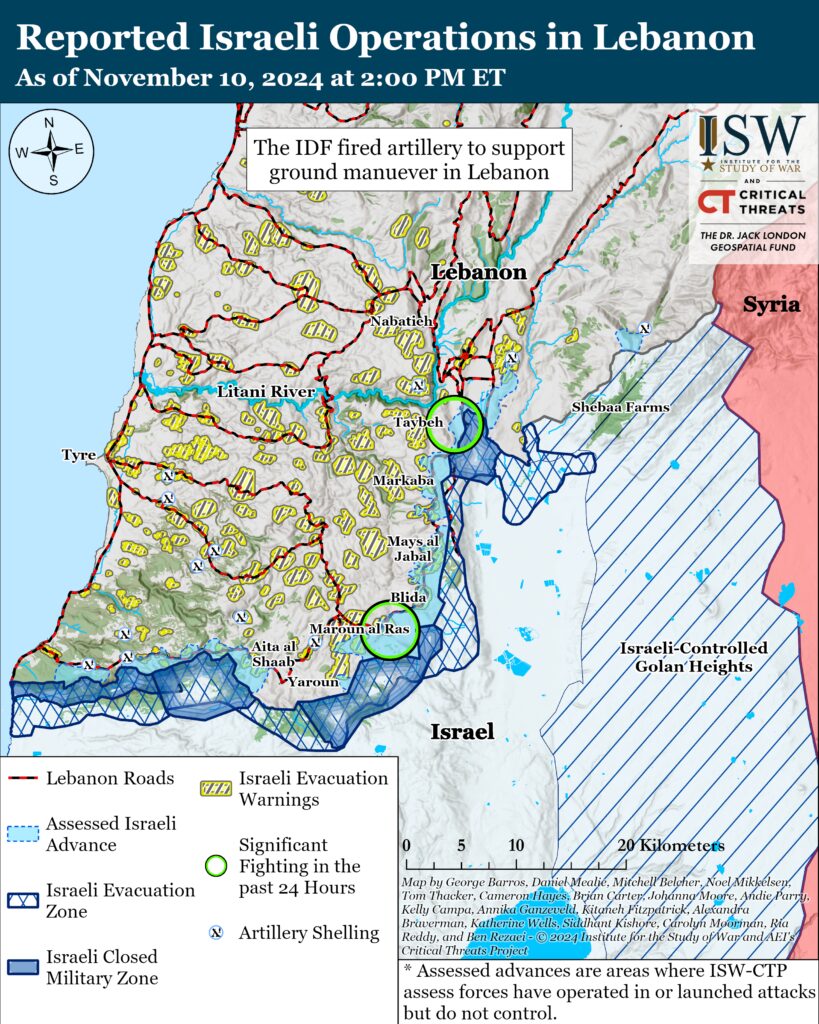
Survive the October 7 War as a capable political and military organization with control over LebanonThe IDF 91st Division has continued clearing operations in southeastern Lebanon.[41] The 91st Division’s Unit 869 identified and killed a Lebanese Hezbollah artillery commander who had fired an anti-tank missile toward Israel.[42] The IDF has so far destroyed dozens of Hezbollah infrastructure sites and launchers using Unit 869 intelligence and has killed numerous Hezbollah fighters.[43]
Hezbollah claimed three attacks targeting the IDF near Kfar Kila on the Israel-Lebanon border on November 10.[44] Hezbollah fired an anti-tank missile targeting Israeli personnel and armor near the border fence.[45] Hezbollah also claimed that it attacked Israeli personnel ”regrouping” near the scene of one of its previous attacks.[46]
Hezbollah claimed that it launched three rocket barrages targeting the IDF on the southeastern outskirts of Markaba, Lebanon, on November 10.[47]

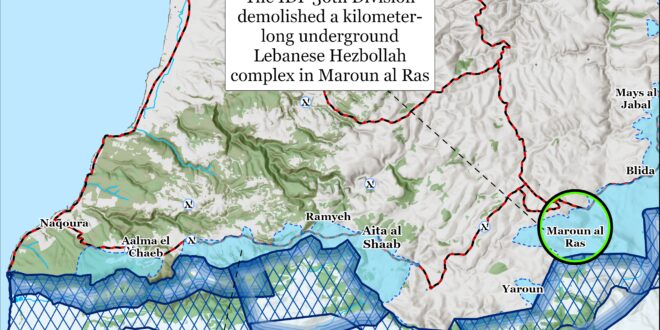
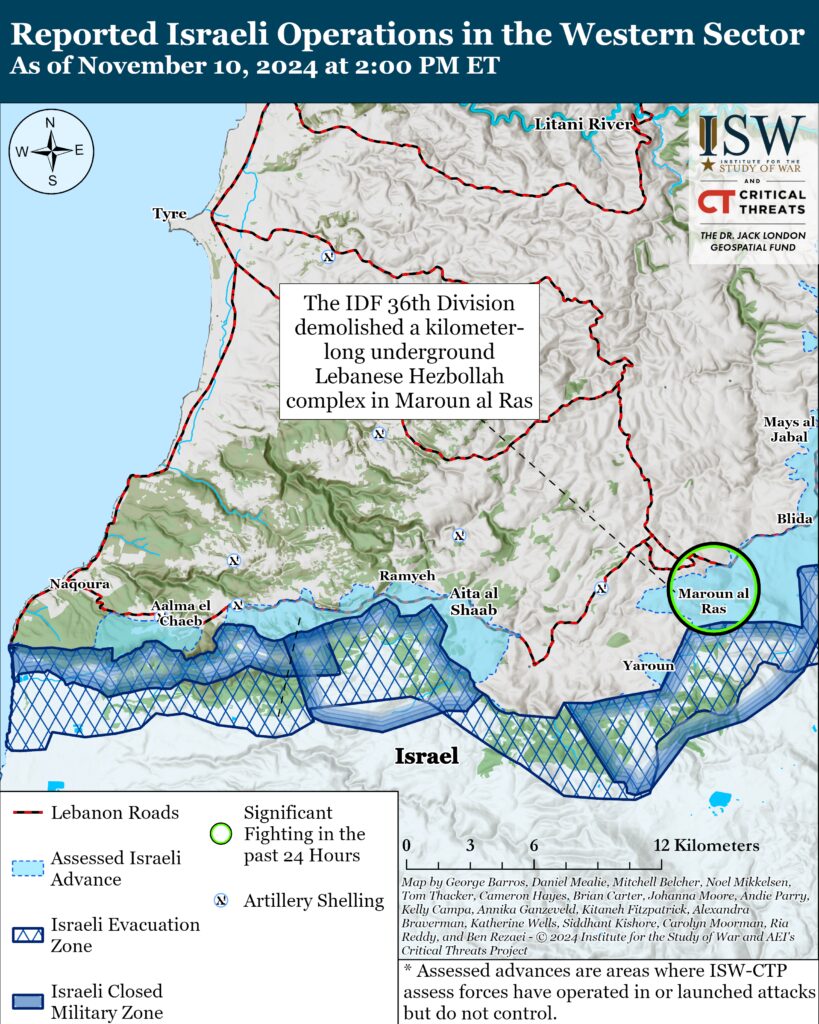
The IDF 36th Division has located and demolished a kilometer-and-a-half-long underground Hezbollah complex in Maroun al Ras over the past week.[48] IDF Unit 5101 identified several shafts that led to the discovery of the route.[49] The IDF located command rooms, living rooms, weapons depots, and combat equipment in the complex that the IDF stated that Hezbollah planned to use in ground attacks into northern Israel.[50] The IDF 1st Infantry Brigade, 282nd Artillery Brigade, Yahalom combat engineers, and 36th Division engineering and logistics units destroyed the complex.[51]
Hezbollah has claimed several attacks targeting the IDF in Aitaroun and Maroun al Ras since CTP-ISW’s last data cutoff on November 9. [52] Hezbollah fired rockets at the IDF south and east of Maroun al Ras.[53] Hezbollah also claimed that it engaged the IDF as it advanced into the southwestern outskirts of Aitaroun.[54] Hezbollah provided no evidence to support this claim.
The IDF continued its air campaign targeting Hezbollah capabilities and infrastructure on November 10. The IDF Air Force struck and killed dozens of Hezbollah fighters in Lebanon in cooperation with IDF Northern Command.[55] The IDF Air Force also struck dozens of targets, including weapons depots, launchers, and launching positions.[56] The Lebanese Health Ministry reported that an Israeli airstrike killed 23 people in Almat, north of Beirut, on November 10.[57]
The IDF Air Force reportedly struck Hezbollah capabilities or personnel outside Damascus on November 10.[58] Local sources reported that the airstrike hit a residential building in Sayyida Zeinab, Rif Dimashq.[59] Several social media users suggested that the strike targeted Hezbollah Golan File commander Ali Mussa Daqduq al Musawi.[60] Musawi directed attacks against hundreds of US servicemembers in Iraq in the 2000s.[61] The IDF nor Hezbollah have commented on the target of the airstrike. The Syrian regime claimed that the strike killed seven civilians and caused material damage to private property.[62] The IDF did not claim the strike but acknowledged on November 5 that its air campaign against Hezbollah includes targeting Hezbollah operations in Syria.[63]
The IDF Air Force likely struck a Syrian regime radar battalion in Suwayda, southern Syria, on November 9.[64] The IDF has repeatedly struck this and similar radar sites in Suwayda.[65] The IDF struck a similar site in Suwayda during its strikes into Iran on October 25.[66]
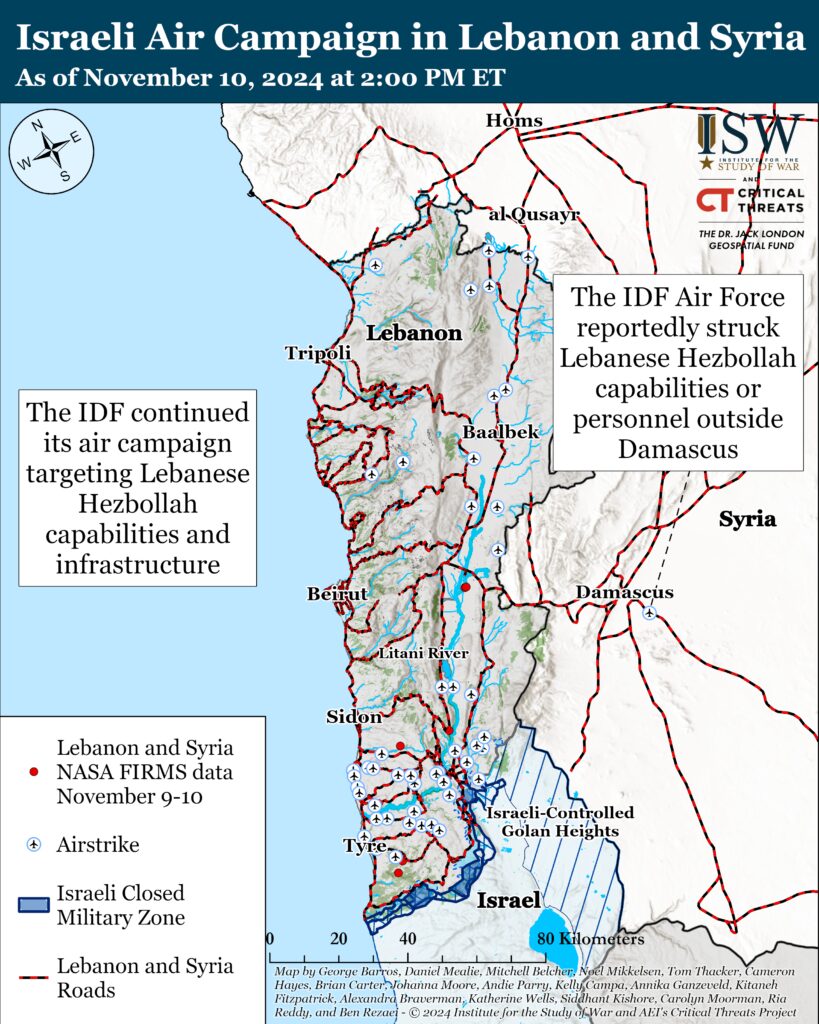
This map illustrates individual Israeli air and artillery strikes based on local Lebanese reporting. This map depicts strikes reported from 2:00pm ET on November 9 to 2:00pm ET on November 10. This map is not exhaustive. CTP-ISW cannot independently verify the locations of Israeli strikes.
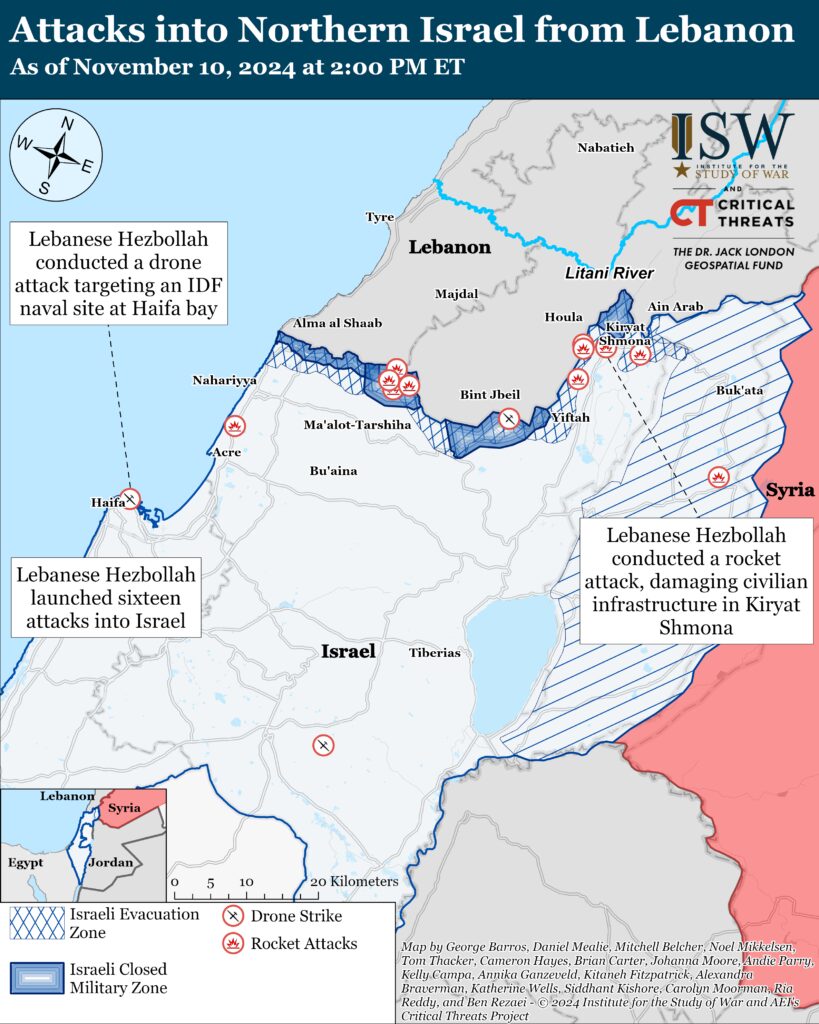
Hezbollah has conducted at least sixteen drone and rocket attacks into Israel since CTP-ISW’s data cutoff on November 9.[67] Hezbollah launched drones targeting an IDF communications base approximately 55 kilometers south of the Israel-Lebanon border on November 9.[68] Hezbollah launched rockets at an IDF reconnaissance base in the Golan Heights for the first time on November 10.[69] Hezbollah separately launched drones targeting an IDF naval site in Haifa bay.[70] The IDF attempted to intercept a drone that crossed into Israeli airspace near Haifa bay and did not report any casualties.[71] A Hezbollah rocket attack targeting Kiryat Shmona damaged civilian infrastructure in the area.[72] Hezbollah launched at least four other drone and rocket attacks targeting civilian sites in northern Israel on November 10.[73]
Iran and the Axis of Resistance
The Islamic Resistance in Iraq—a coalition of Iranian-backed Iraqi militias—claimed a drone attack targeting an unspecified “vital target” in southern Israel on November 9.[74] The Iranian-backed Iraqi militia Saraya Awliya al Dam, which claims to be affiliated with the Islamic Resistance of Iraq, separately claimed drone attacks targeting three unspecified ”vital targets” in Israel on November 10.[75] The IDF stated that it intercepted a drone from the east before it entered Israeli airspace on November 10.[76] Parts of the intercepted drone fell into an open area in the Golan Heights.
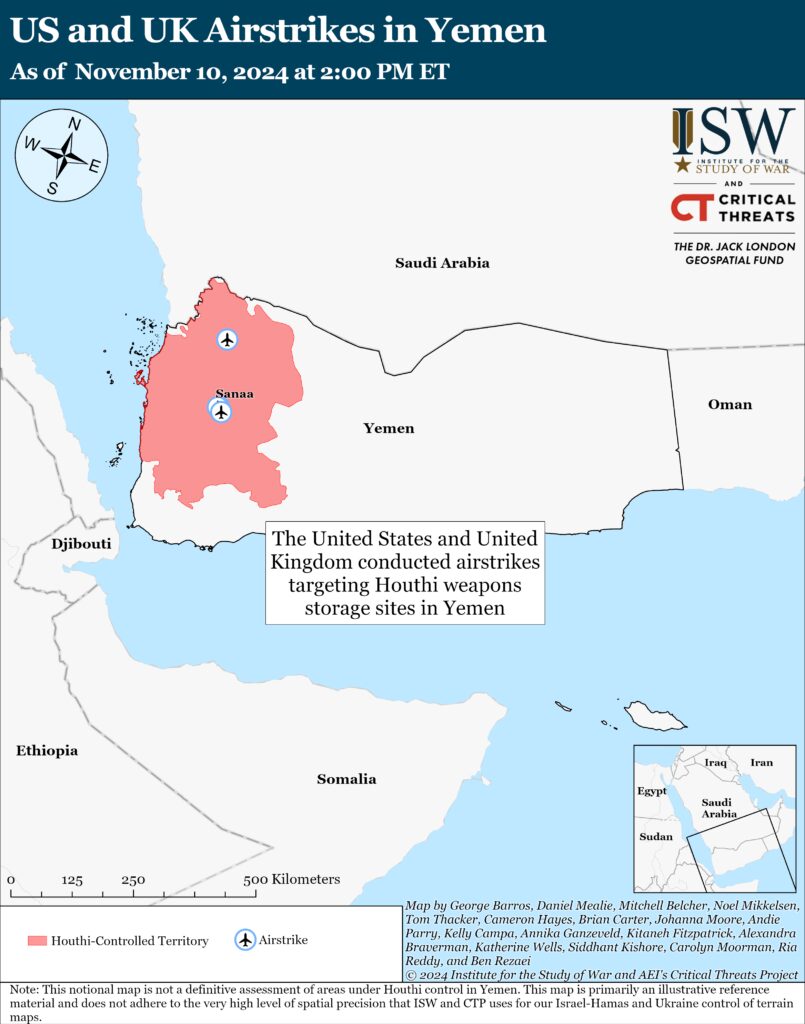
The United States and United Kingdom conducted several airstrikes targeting Houthi weapons storage sites in Yemen on November 9.[77] Local Yemeni sources reported several US-UK airstrikes in al Hafa and al Nahadin neighborhoods in Sanaa on November 9.[78] Local Yemeni sources also reported four US-UK airstrikes targeting Houthi positions in Sanhan and Bani Bahlul district in Sanaa governorate and two airstrikes on Harf Sufyan district in Amran governorate, north of Sanaa, on November 9.[79]
The Iran Update provides insights into Iranian and Iranian-sponsored activities abroad that undermine regional stability and threaten US forces and interests. It also covers events and trends that affect the stability and decision-making of the Iranian regime. The Critical Threats Project (CTP) at the American Enterprise Institute and the Institute for the Study of War (ISW) provides these updates regularly based on regional events.
CTP-ISW defines the “Axis of Resistance” as the unconventional alliance that Iran has cultivated in the Middle East since the Islamic Republic came to power in 1979. This transnational coalition is comprised of state, semi-state, and non-state actors that cooperate to secure their collective interests. Tehran considers itself to be both part of the alliance and its leader. Iran furnishes these groups with varying levels of financial, military, and political support in exchange for some degree of influence or control over their actions. Some are traditional proxies that are highly responsive to Iranian direction, while others are partners over which Iran exerts more limited influence. Members of the Axis of Resistance are united by their grand strategic objectives, which include eroding and eventually expelling American influence from the Middle East, destroying the Israeli state, or both. Pursuing these objectives and supporting the Axis of Resistance to those ends have become cornerstones of Iranian regional strategy.
 Eurasia Press & News
Eurasia Press & News