Since Israel’s assault on Gaza began, three separate polls show that Arab and Muslim populations are shifting their support away from Washington’s regional allies toward West Asia’s Axis of Resistance.
It could be a clean sweep. Decades of western-led narratives crafted to exploit differences throughout West Asia, create strife amid the region’s myriad communities, and advance western foreign policy objectives over the heads of bickering natives are now in ruins.
The war in Gaza, it transpires, has blown a mile-wide hole in the falsehoods and fairytales that have kept West Asia distracted with internecine conflicts since at least the 1979 Islamic Revolution in Iran.
Shia versus Sunni, Iran versus Arabs, secular versus Islamist: these are three of the west’s most nefarious narrative ploys that sought to control and redirect the region and its populations, and have even drawn Arab rulers into an ungodly alliance with Israel.
Facts are destroying the fiction
It took a rare conflict – uncooked and uncontrolled by Washington – to liberate West Asian masses from their narrative trance. Israel’s genocidal assault on Gaza also brought instant clarity to the question of which Arabs and Muslims actually support Palestinian liberation – and which do not.
Iran, Hezbollah, Iraqi resistance factions, and Yemen’s Ansarallah – maligned by these western narratives – are now visibly the only regional players prepared to buttress the Gaza frontline, whether through funds, weapons, or armed clashes that aim to dilute and disperse Israeli military resources.
The so-called ‘moderate Arabs,’ a misnomer for the western-centric, authoritarian Arab dictatorships subservient to Washington’s interests, have offered little more than lip service to the carnage in Gaza.
The Saudis called for support by hosting Arab and Islamic summits that were allowed to do and say nothing. The Emiratis and Jordanians trucked supplies to Israel that Ansarallah blockaded by sea. The mighty Egypt hosted delegations when all it needed to have done was to open the Rafah Crossing so Palestinians can eat. Qatar – once a major Hamas donor – now negotiates for the freedom of Israeli captives, while hosting Hamas ‘moderates,’ who are at odds with Gaza’s freedom fighters. And Turkiye’s trade with the Israeli occupation state continues to skyrocket (exports increased 35 percent from November to December 2023).
Palestine, for the pro-west ‘moderate Arabs,’ is a carefully handled flag they occasionally wave publicly, but sabotage privately. So, they watch, transfixed and horrified today, at what social media and tens of millions of protesters have made crystal clear: Palestine remains the essential Arab and Muslim cause; it may ebb and flow, but nothing has the power to inflame the region’s masses like this particular fight between right and wrong.
The shift toward resistance
It is early days yet in the battle unfolding between the region’s Axis of Resistance and Israel’s alliances, but the polls already show a notable shift in public sentiment toward the former.
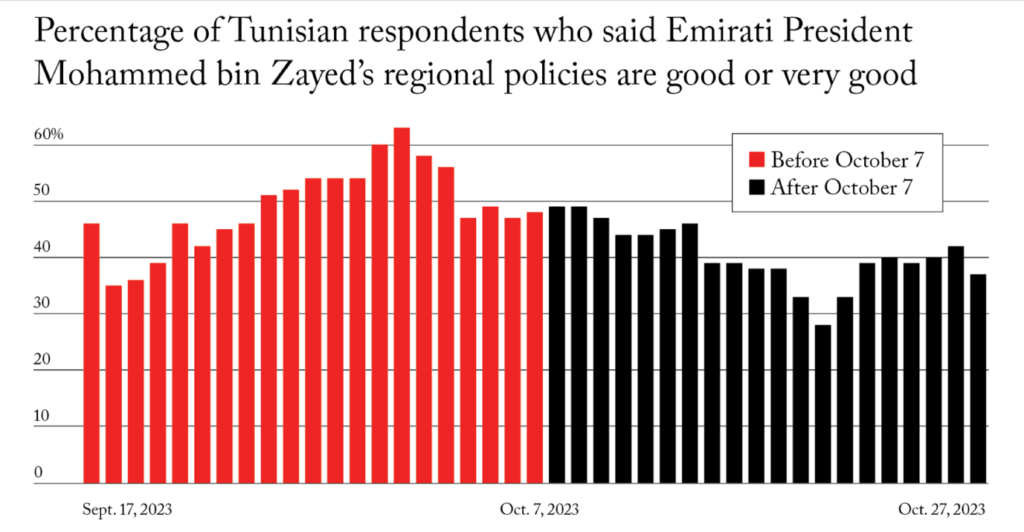
An Arab barometer poll taken over a six-week period – three weeks before and three weeks after the Al-Aqsa Flood operation – provides the first indication of shifting Arab perceptions. Although the survey was restricted to Tunisia, the pollsters argue that the country is “as close to a bellwether as one could imagine” and that it represents views similar to other Arab countries:
“Analysts and officials can safely assume that people’s views elsewhere in the region have shifted in ways similar to the recent changes that have taken place in Tunisia.”
The survey results should be of paramount concern to meddling western policymakers: “Since October 7, every country in the survey with positive or warming relations with Israel saw its favorability ratings decline among Tunisians.”
The US saw its favorability numbers plummet the most, followed by West Asian allies that have normalized relations with Israel. Russia and China, both neutral states, experienced little change, but Iran’s leadership saw its favorability figures rise. According to the Arab barometer:
“Three weeks after the attacks, Iranian Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei has approval ratings that matched or even exceeded those of Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman and Emirati President Mohammed bin Zayed.”
Before 7 October, just 29 percent of Tunisians held a favorable view of Khamenei’s foreign policies. This figure rose to 41 percent according to the conclusion of the survey, with Tunisian support most notable in the days following the Iranian leader’s 17 October reference to Israel’s actions in Gaza as a “genocide.”

The Saudi shift
Prior to the 7 October operation by the Palestinian resistance to destroy the Israeli army’s Gaza Division and take captives as leverage for a mass prisoner swap, the region’s main geopolitical focus was on the prospects of a groundbreaking Saudi normalization deal with Tel Aviv. The administration of US President Joe Biden flogged this horse at every opportunity; it was seen as a golden ticket for his upcoming presidential election.
But Operation Al-Aqsa Flood ruined any chance for Saudi Arabia – home to Islam’s holiest sites – to seal that political deal. And with Israeli airstrikes raining down daily on Palestinian civilians in Gaza, Riyadh’s options continue to shrink.
A Washington Institute poll conducted between 14 November and 6 December measures the seismic shift in Saudi public sentiment:
A whopping 96 percent agree with the statement that “Arab countries should immediately break all diplomatic, political, economic, and any other contacts with Israel, in protest against its military action in Gaza.”
Meanwhile, 91 percent believe that “despite the destruction and loss of life, this war in Gaza is a win for Palestinians, Arabs, and Muslims.” This is a shockingly unifying statement for a country that has adhered closely to western narratives that seek to divide Palestinians from Arabs, Arabs among themselves, and Muslims along sectarian lines – geographically, culturally, and politically.
Although Saudi Arabia constitutes one of the few Arab states to have designated Hamas as a terrorist organization, favorable views of Hamas have increased by 30 percent, from 10 percent in August to 40 percent in November, while most – 95 percent – do not believe the Palestinian resistance group killed civilians on 7 October.
Meanwhile, 87 percent of Saudis agree with the idea that “recent events show that Israel is so weak and internally divided that it can be defeated some day.” Ironically, this is a long-stated Resistance Axis refrain. Hezbollah Secretary General Hassan Nasrallah was famously quoted as saying “Israel is weaker than a spider’s web,” upon its defeat by the Lebanese resistance on 25 May, 2000.
Prior to 7 October, Saudis had strongly favored economic ties with Israel, but even that number dropped dramatically from 47 percent last year to 17 percent today. And while Saudi attitudes toward the Resistance Axis remain negative – Saudi Arabia, after all, has been the regional epicenter for anti-Iran and anti-Shia propaganda since the 1979 revolution – that may be largely because their media is heavily controlled. Contrary to the observations of the Arab masses, 81 percent of Saudis still believe that the Axis is “reluctant to help Palestinians.”
The Palestinian shift
Equally important to the discussion of Arab perceptions is the shift seen among Palestinians themselves since 7 October. A poll conducted by the Palestinian Center for Policy and Survey Research (PSR) in both the occupied West Bank and Gaza Strip between 22 November and 2 December mirrors Arab views, but with some nuances.
Gazan respondents, understandably, displayed more skepticism for the ‘correctness’ of Hamas’ Operation Al-Aqsa Flood, which triggered Israel’s genocidal assault on the Strip in which over 22,000 civilians – mostly women and children – have so far been brutally killed. While support for Hamas increased only slightly in the Gaza Strip, it tripled in the West Bank, with both Palestinian territories expressing near equal disdain for the western-backed Palestinian Authority (PA), which governs from Ramallah.
Support for acting PA President Mahmoud Abbas and his Fatah party was hit hard. Demands for his resignation are at nearly 90 percent, while almost 60 percent (the highest number recorded in a PSR poll to date in relation to this matter) of those surveyed want a dissolution of the PA.
Over 60 percent of Palestinians polled (closer to 70 percent in the West Bank) believe armed struggle is the best means to end the occupation, with 72 percent agreeing with the statement that Hamas made a correct decision to launch its 7 October operation, and 70 percent agreeing that Israel will fail to eradicate the Palestinian resistance in Gaza.
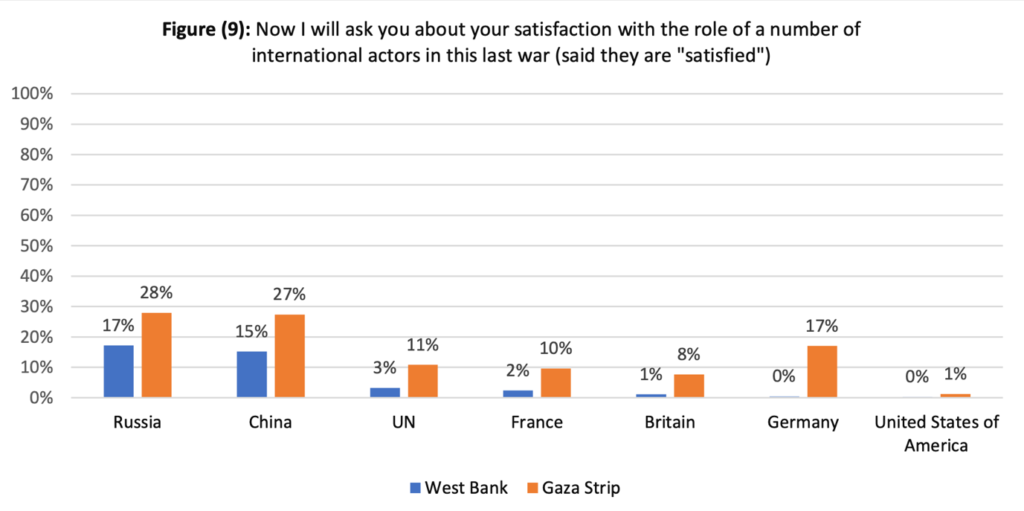
Palestinians have strong views about regional and international players, who they largely feel have left Gaza unprotected from Israel’s unprecedented violations of international law.
By far the country most supported by respondents is Yemen, with approval ratings of 80 percent, followed by Qatar (56 percent), Hezbollah (49 percent), Iran (35 percent), Turkiye (34 percent), Jordan (24 percent), Egypt (23 percent), the UAE (8 percent), and Saudi Arabia (5 percent).

In this poll, the region’s Axis of Resistance dominates the favorability ratings, while pro-US Arab and Muslim nations with some degree of relations with Israel, fare poorly. It is notable that of the four most favorable countries and groups for mostly-Sunni Palestinians, three are core members of the “Shia” Axis, while five Sunni-led states rank lowest.
This Palestinian view extends to non-regional international states, with respondents most satisfied with Resistance Axis allies Russia (22 percent) and China (20 percent), while Israeli allies Germany (7 percent), France (5 percent), the UK (4 percent), and the US (1 percent) struggle to maintain traction among Palestinians.
The numbers depend on the war ahead
Three separate polls show that Arab perceptions have shifted dramatically over Israel’s war on Gaza, with popular sentiment gravitating to those states and actors perceived to be actively supporting Palestinian goals, and away from those who are perceived to support Israel.
The new year starts with two major events. The first is the drawdown of Israeli reservists from Gaza, whether because Washington demands it, or due to unsustainable loss of life and injury to occupation troops. The second is the shocking assassination of Hamas leader Saleh al-Arouri and six others in Beirut, Lebanon, on 2 January.
All indications are that Israel’s war will not only continue, but will expand regionally. The new US maritime construct in the Red Sea has drawn other international actors into the mix, and Tel Aviv has provoked Lebanon’s Hezbollah in a major way.
But if the confrontation between the two axes escalates, Arab perceptions will almost certainly continue to tilt away from the old hegemons toward those who are willing to resist this US-Israeli assault on the region.
There will be no relief for Washington and its allies as the war expands. The more they work to defeat Hamas and destroy Gaza, and the more they lob missiles at Yemen, Iraq, and Syria, and besiege the Resistance Axis, the more likely Arab populations are to shrug off the Sunni-versus-Shia, Iran-versus-Arab, and secular-versus-Islamist narratives that have kept the region divided and at odds for decades.
The swell of support that is mobilizing due to a righteous confrontation against the region’s biggest oppressors is unstoppable. Western decline is now a given in the region, but western discourse has been the first casualty of this war.
 Eurasia Press & News
Eurasia Press & News




