Competition over the world’s maritime resources and territorial disputes over maritime borders are becoming increasingly prominent in international affairs. At the same time, depleted fish stocks and polluted waters make the question of how countries can collectively manage maritime resources a central one, particularly in discussions over climate change.
Against the backdrop of heightened competition in the maritime domain, China has been rapidly modernizing and expanding its naval capabilities thanks to an unprecedented shipbuilding effort. By contrast, the U.S. Navy is struggling to meet its ambitious goals toward expanding its fleet while nevertheless maintaining a demanding operational tempo.
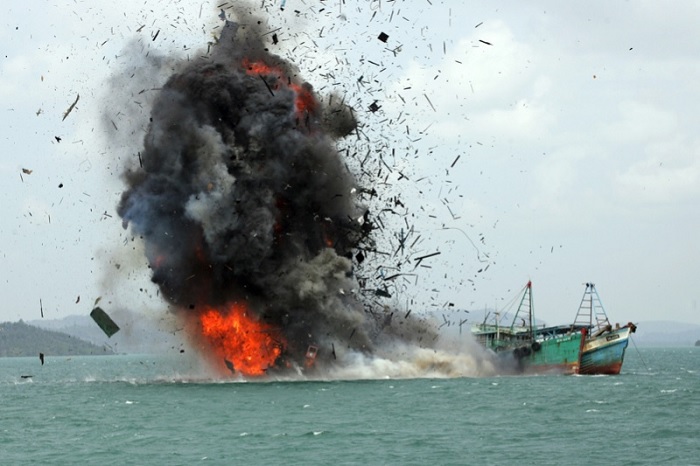
Meanwhile, the resources that lie beneath the ocean’s surface are increasingly at risk of overexploitation. Illegal fishing is devastating already diminished global stocks and may soon present a severe crisis to countries whose populations depend on seafood for their diets. In the South China Sea, competition over fishing rights as well as offshore oil and gas reserves has been a major driver of tensions and conflict.
The maritime domain highlights the tensions between national sovereignty and transnational challenges, between the ocean’s littoral regions as exclusive economic zones and the high seas as a global commons. While often ignored in coverage of international affairs, it features prominently in bilateral, regional and multilateral diplomacy, particularly when it comes to resolving boundary disputes.
WPR has covered maritime issues in detail and continues to examine key questions about what will happen next. Will the United States shore up its naval superiority or continue to cede ground to China? How will the pivot to renewable resources affect competition for maritime resources? Will concerns over climate change and depleting fish stocks jumpstart global efforts to improve the state of the world’s oceans?
 Eurasia Press & News
Eurasia Press & News