It remains an open question whether differing ethnic and/or religious groups – tribes if you will – can share a state without conflict turning into ethnic cleansing. Since antiquity, history offers few examples except at times in large multi-ethnic empires such as the Roman, Ottoman and American. Even in the American, recent days showcase often vicious White nationalism and intolerant Christian fundamentalism tearing at the fabric of the political system. Kosovo and Nagorno-Karabakh raise this question afresh.
Azerbaijan is an overwhelmingly Muslim and Turkic country while the enclave’s Armenians are Christians who have lived there for millennium. The seizure of Nagorno-Karabakh by the Azerbaijan military is reportedly leading many of the enclaves 120,000 Armenians to consider leaving. Azerbaijan – an authoritarian, family-ruled state – claims it wants to integrate them as “equal citizens.” But the Armenians fear – not without reason given Azerbaijan’s destruction of centuries-old churches in areas captured in the 2020 war – being eventually cleansed. The Armenians of Nagorno-Karabakh are isolated as the enclave does not share a land border with Armenia proper. They have little choice but to risk staying or leave for Armenia.
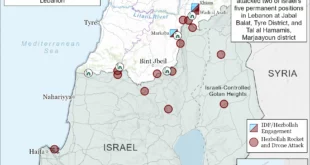
Kosovo is overwhelmingly Albanian and Muslim. Northern Kosovo is majority Serbian and Christian. The political status of Kosovo remains unsettled since 1999 and the conflict between Serbs and Albanians there is considerably older. The Albanian-nationalist Kurti regime has upped the ante this past year by seeking to use its police to take control of the north away from local Kosovo Serb authorities. The U.S., EU and NATO prevented Kurti accomplishing his immediate aims but continue to fail to resolve the underlying status issue. Now, a reported standoff between Kosovo police and armed men at or near a monastery in the north where Serbian pilgrims were visiting. A policeman and at least three of the armed men reportedly were killed before police were able to enter the monastery. NATO forces are at the scene. I don’t know the details of this particular conflict – what and who led to what. But it was clear to me when I arrived as UNKIK’s regional representative in Mitrovica in 2005 that most Albanians deeply resented the continued presence of Serbs north of the Ibar and want them gone.
The northern Kosovo Serb enclave has a land connection to Serbia proper. It is time to recognize that the U.S. and EU efforts to win agreement between Belgrade and Pristina or make Kosovo into a peaceful multi-ethnic state go nowhere. The Quint powers that enabled Kosovo independence must now face the reality that it won’t work until Serbian security returns to the north and it becomes fully part of Serbia again. This may leave the remaining Kosovo Serbs south of the Ibar at some risk. But even Kurti may recognize the business possibilities of preserving the cultural sites and places such as Štrpce for tourism.
 Eurasia Press & News
Eurasia Press & News